 |
Geoscience Education in the Mountain State: |
| CATS Earth Science Connections III |
| Environmental Geology Telecourse |
Weekly Course Notes: October 8, 2001 (Show 4)
Outline
Dr. Deb and Dr. Bob
- Volcanoes: Hollywood Films to Promote Inquiry in the Classroom
- Linking Topics: Mt. St. Helens, Earthquakes, Landslides, Eruptions
- Class Requirements
- Quizzes
- Project
- Field Trip
Break
Dr. Jack and Dr. Bob
- Weathering: Physical and Chemical
- Erosion by Fluids in Motion and Gravity
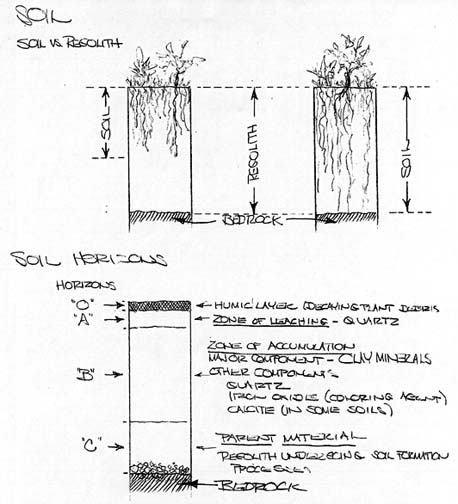
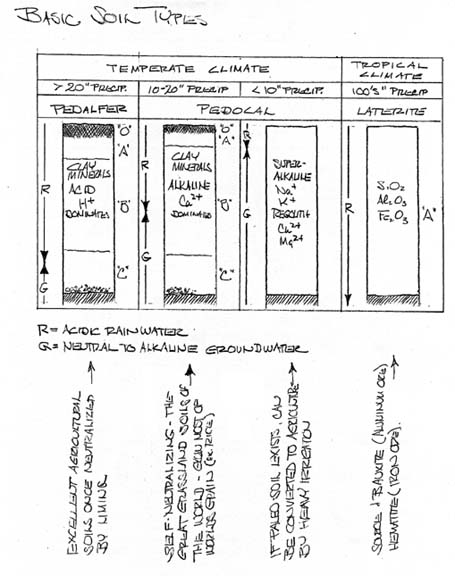
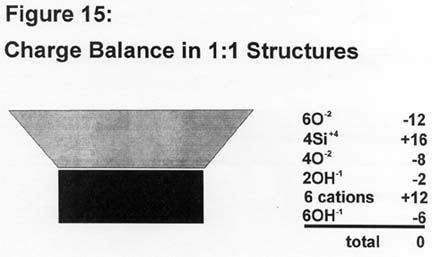
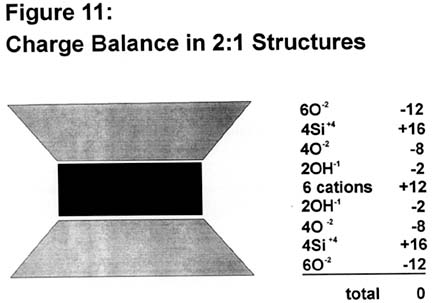
- Clay Minerals: The Weathering of Feldspars
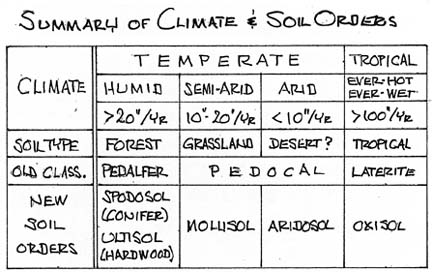
- Soils S=f(Cl, O, R, P, T)
- Mass Movement
- Subsidence: Natural and Human-Induced
- Preview of Show #5: Climate Changes---El Nino, La Nina, and the Big Picture: Desertification, Glaciations, etc.
Volcanic Inquiry Using Hollywood Movies
List the eruption precursors mentioned in the movie and the cause attributed to each:
| Warning Signs Illustrated in Movie |
Cause Attributed in Movie |
Seismic activity
Frequency (25-80)
Depth (10-20 km Shallow)
Magnitude2.9 |
Magmatic
(USGS boss claimed Tectonic) |
Hot springs present
Swimmers boiled to death |
Hydrothermal activity |
Acidity of mountain water increased
pH measured 3.49 |
_ |
| Trees recently dead on hillside |
CO2 emissions |
| Dead squirrels all over mountain |
CO2 emissions |
| Sulfur dioxide gas released into water |
_ |
| Landslides within crater |
Earthquake triggered |
| Lava dome |
_ |
- Measurements recorded by vulcanologists:
- SO2 monitored (via chopper)
- Seismographs
- pH
- Tiltmeter (doming of mountain)
- Robotic video
- Remote gas sensors on robot
- Sociological problems:
- Town at great risk due to location at the base of a "chute"
- Town resistant to evacuation (loss of grant monies)
- Cannot predict with certainly when the mountain will erupt
- USGS sensitive to false alarms after Mammoth Lakes incident
- Residents simple refusal to leave high-risk areas
- Characteristics of the eruption:
- Ash blowing out the top of the volcano at the onset
- Earthquakes generated strong enough to topple buildings
- Firey volcanic bombs and blocks striking town
- Light is blocked and the area becomes dark
- Ash too thick to see through
- Lightning
- Magma spewing out of fissure
- Thin lava flows moving rapidly
- Mountain lake acidifies, killing fish and dissolving props off boat motor
- Lahars---mudflows as snowpack melts
- Flooding rivers laden with debris, taking out dams and bridges
- Tremendous explosion emitting a cloud knocking down anything in its path
- Student-generated questions?
- Could the lake really dissolve your grandmother's leg?
- Could this happen in the United States?
- Can a truck with rubber tires and a loaded gas tank REALLY cross a river of lava?
- How do most people die in volcanic eruptions?
- Was this real?
- Why don't we have volcanoes here?
- Chemical weathering
- Oxidation
- Dissolution
- Carbonation/Hydrolysis
- Oxidation
- Fe + O2
 Fe2O3
Fe2O3
- 4Fe + 3O2 + 2H2O
 4FeOOH (Limonite ~ Yellow Boy)
4FeOOH (Limonite ~ Yellow Boy)
- 2FeOOH
 Fe2O3 + H2O (Hematite)
Fe2O3 + H2O (Hematite)
- Carbonic Acid
- H2O + CO2
 H2CO3
H2CO3
- H2CO3
 H+ + HCO3
H+ + HCO3
- Dissolution
CaCO3 + H+ + HCO3  Ca2+ +2HCO3- (Calcite)
Ca2+ +2HCO3- (Calcite)

Links
USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service
Dr. Robert Behling (rbehling@wvu.edu)
WVGES Welcome Page
Geoscience Education Main
Environmental Geology Main
Page last revised: October 31, 2001
Please send questions, comments, and/or suggestions to webmaster@wvgs.wvnet.edu







